Playground
The Playground provides an interactive testing environment where you can quickly test guardrails and applications without writing code. It's accessible from the admin interface and supports both individual guardrail testing and complex DAG workflow execution.
Overview
The Playground offers two main testing modes:
- Guardrail Testing: Test individual guardrails with specific inputs
- Application Testing: Execute complete DAG workflows with orchestrated guardrail combinations
Using the Playground
Accessing the Playground
Navigate to the Playground tab in the admin interface to access the testing environment.
Input Fields
The Playground provides three main input fields that correspond to the Entailment Frame data structure:
- Context: Background information, documents, or knowledge relevant to the verification task
- Question: The specific question being asked about the context or that needs verification
- Answer: The answer or output that should be verified by the guardrail
Note: Depending on the selected target (guardrail type or application), some fields may be automatically hidden if they're not required for that specific verification type.
Target Selection
Use the Select Target dropdown to choose what you want to test:
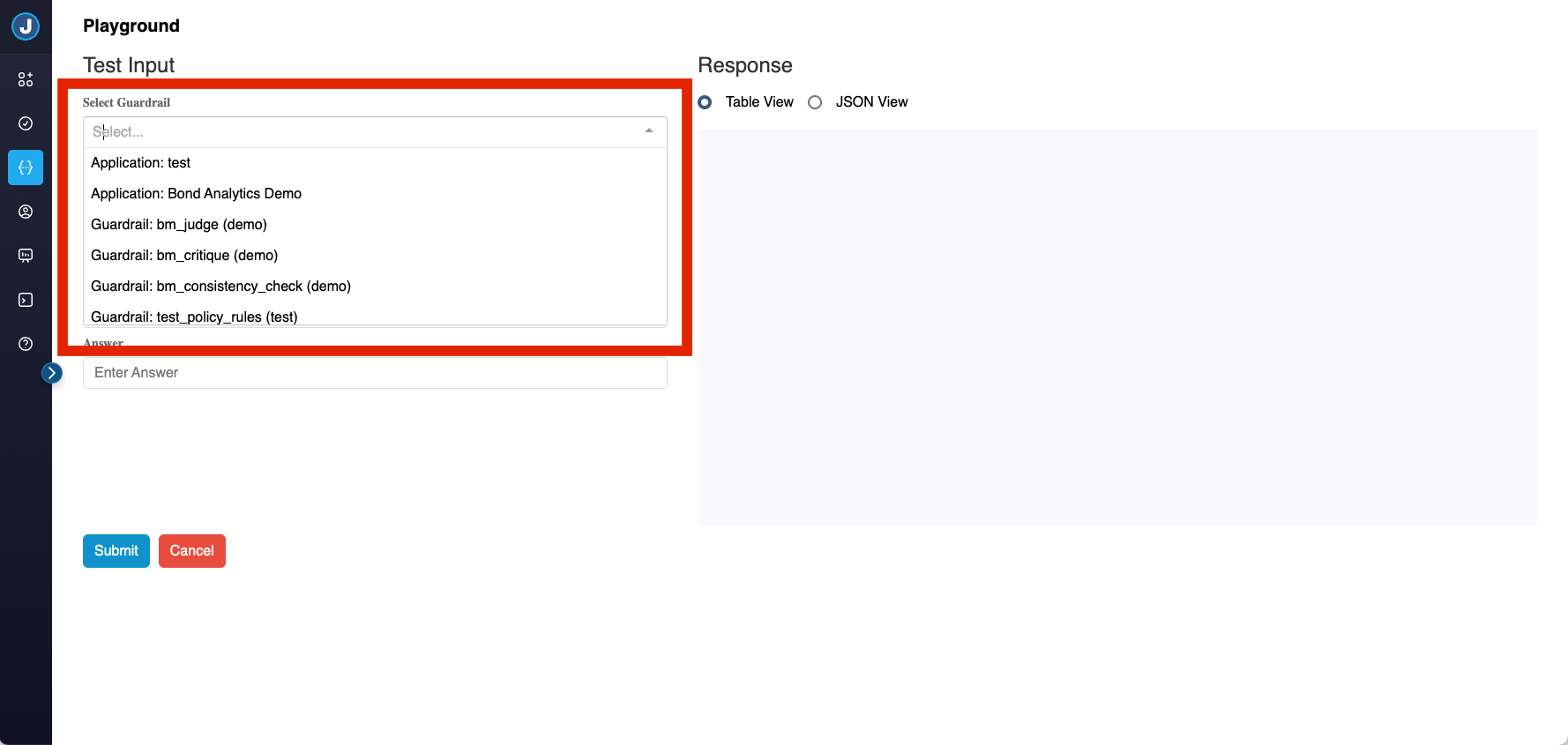
Available Targets:
- Applications: Execute DAG workflows that combine multiple guardrails
- Individual Guardrails: Test specific guardrails in isolation
Target Status Indicators:
- ✅ Complete Targets: Fully configured and ready to run
- ⚠️ Incomplete Targets: Missing required configuration (cannot be executed)
Response Views
The Playground offers two different ways to view results:
Table View (Default)
The Table View provides a clean, formatted display of the verification results:
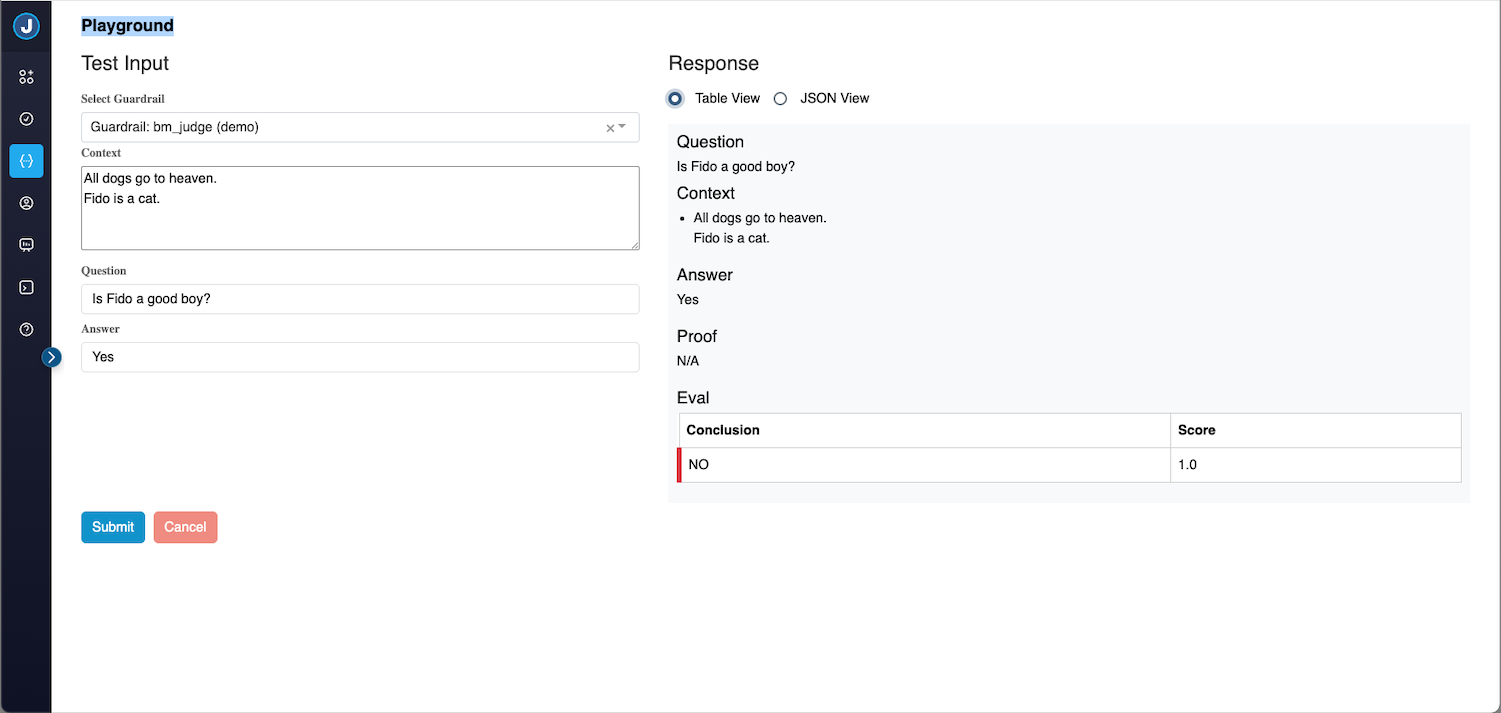
Table View Features:
- Structured Display: Results organized into clear sections (Question, Context, Answer, Proof, Eval)
- Smart Hiding: Empty sections are automatically hidden rather than showing "N/A"
- Table Formatting: Complex answers are displayed in readable tables when applicable
- Visual Clarity: Color-coded sections and proper spacing for easy reading
Policy Rules Guardrails - Enhanced Display:
When testing Policy Rules guardrails, the Table View provides a specialized rule-oriented display:
- Rule Cards: Each policy rule appears as a collapsible card with a pass/fail indicator (✓ or ❌)
- Rule Text: The original natural language rule is displayed as the card header
- DSL Code: The formalized DSL code for each rule is shown in a syntax-highlighted editor
- Rule-Scoped Questions: Only questions relevant to that specific rule's variables are shown (not all global questions)
- Combined Assertions: If a rule contains multiple DSL assertions, they're evaluated together - ❌ appears if ANY assertion fails, ✓ only if ALL pass
JSON View
The JSON View shows the raw JSON response data for technical analysis:
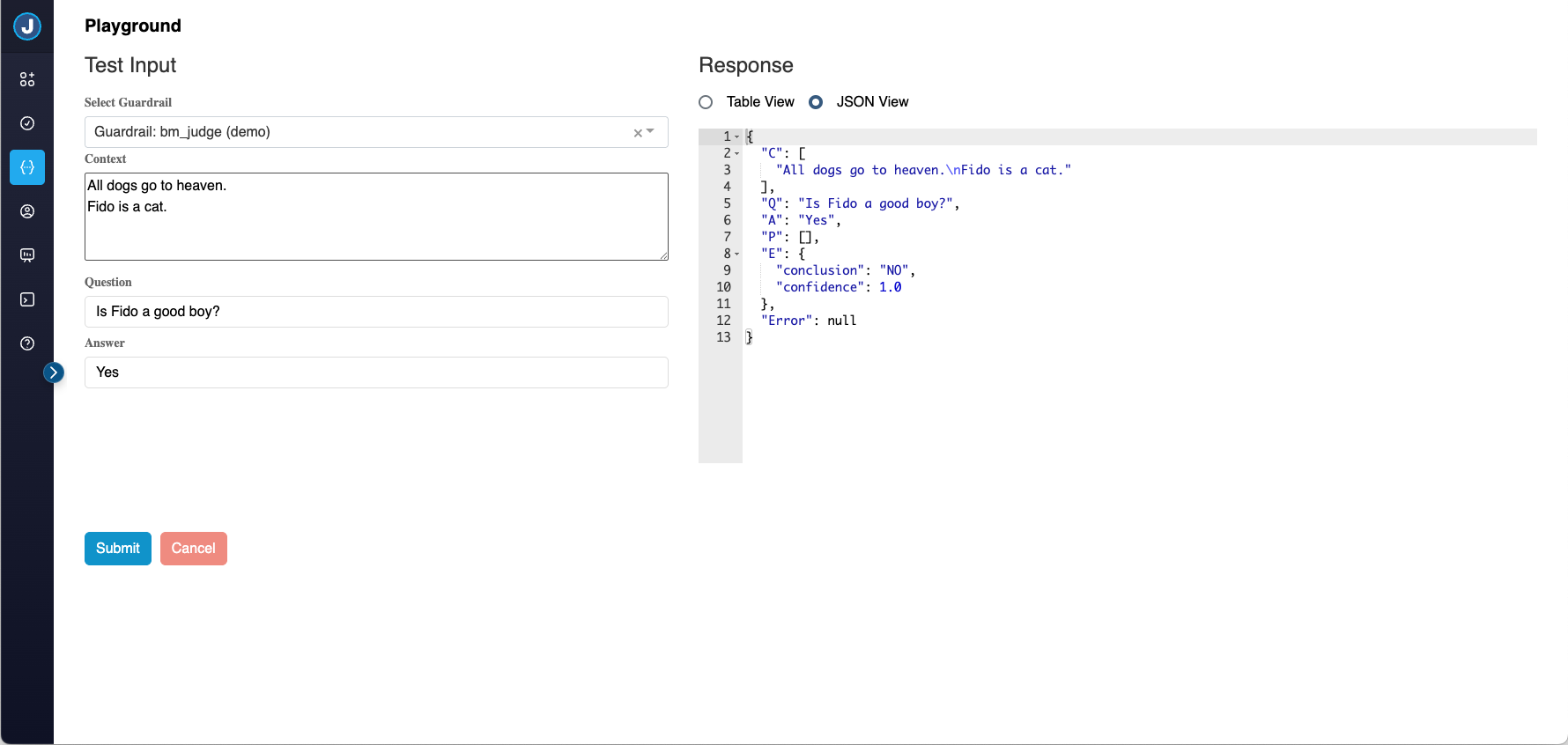
JSON View Features:
- Complete Data: Shows the full response structure including all metadata
- Syntax Highlighting: Properly formatted JSON with syntax coloring
- Read-Only Editor: Built on ACE editor for professional JSON viewing
- Raw Access: Unprocessed response data for debugging and integration
Testing Workflow
Step 1: Select Target Choose the guardrail or application you want to test from the dropdown.
Step 2: Provide Input Fill in the relevant input fields based on your verification scenario:
- Context: Add any background documents or information
- Question: Specify what you're trying to verify
- Answer: Provide the output that needs verification
Step 3: Submit Request Click Submit to execute the verification. The Playground will:
- Send your input to the selected target
- Display a loading indicator while processing
- Return the verification results
Step 4: Review Results Switch between Table View and JSON View to analyze the results:
- Use Table View for human-readable verification outcomes
- Use JSON View for technical details and integration planning
Advanced Features
Request Management
Cancel Requests: Use the Cancel button to stop long-running requests before they complete.
Timeout Handling: Requests will automatically timeout if they don't complete within the configured time limit.
Response Analysis
Confidence Scores: Many guardrails provide confidence scores on a scale from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates the highest confidence.
Proof Steps: Detailed reasoning steps showing how the guardrail reached its conclusion.
Error Handling: Clear error messages when guardrails encounter issues or incomplete configurations.
Testing Strategies
Individual Guardrail Testing
Basic Verification Testing: 1. Start with simple, known examples where you expect specific outcomes 2. Test edge cases and boundary conditions 3. Verify that confidence scores align with expected certainty levels 4. Check that proof steps provide logical reasoning
Iterative Refinement: 1. Test guardrail with initial configuration 2. Analyze results and identify areas for improvement 3. Adjust guardrail settings based on findings 4. Re-test to validate improvements
Application DAG Testing
Component Testing: 1. Test individual guardrails separately before combining them in DAGs 2. Verify each guardrail works correctly with your specific input patterns 3. Understand the output format of each component
Integration Testing: 1. Test simple DAG configurations with 2-3 guardrails 2. Verify that data flows correctly between nodes 3. Check that aggregation logic produces expected results 4. Gradually add complexity as confidence builds
End-to-End Validation: 1. Test complete workflows with realistic production data 2. Verify performance characteristics under load 3. Validate that final outputs meet business requirements
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
"Incomplete Target" Warnings: - Ensure all required fields are configured for the selected guardrail - Check that the guardrail has been properly saved and validated - Verify that any referenced resources (like LLM models) are available
Timeout Errors: - Complex DAGs may require longer processing time - Check system resources and load - Consider simplifying the DAG or optimizing individual guardrails
Connection Issues: - Verify that all backend services are running properly - Check network connectivity between components - Review system logs for detailed error information
Debugging Tips
Use JSON View: - Review the complete response structure for debugging information - Look for error messages in the response metadata - Analyze intermediate results in complex DAG workflows
Test Incrementally: - Start with simple inputs and gradually increase complexity - Test individual components before testing integrated workflows - Use known good examples to validate system functionality
Monitor Performance: - Track response times for different types of requests - Identify bottlenecks in complex DAG configurations - Use the information to optimize guardrail and DAG designs
Best Practices
Input Preparation
- Use realistic examples that represent actual production scenarios
- Keep context focused and relevant to avoid confusion
- Test with various input sizes to understand performance characteristics
Result Interpretation
- Don't rely solely on confidence scores - review the reasoning in proof steps
- Test multiple similar examples to ensure consistent behavior
- Consider edge cases and unusual input patterns
Testing Workflow
- Document test cases and expected outcomes for repeatable testing
- Maintain a library of standard test scenarios for regression testing
- Regularly re-test guardrails as configurations evolve
Performance Considerations
- Be mindful of timeout settings for complex DAGs
- Test with production-like data volumes when possible
- Consider the impact of parallel execution in DAG designs